Fraunhofer Diffraction
Fraunhofer Diffraction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Intensity of Diffraction Pattern in Fraunhofer's diffraction, Fraunhofer Shape of Incident or Diffracted Wavefront, Position of Secondary Maximum in Fraunhofer Diffraction, etc.
Important Questions on Fraunhofer Diffraction
A single slit diffraction pattern is formed using white light. For what wavelength does the third minimum coincide with the second secondary maximum produced by wavelength of ?
Diffraction pattern from a single slit is shown in the figure. The point at which the path difference between two extreme rays from the slit is twice the wavelength is given by the point
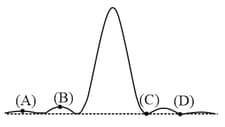
A diffraction pattern obtained from a double slit illuminated with monochromatic light is shown in the figure. The dotted line in the figure shows the diffraction envelope while the solid lines give the double slit interference fringes. The experimenter has an arrangement to keep the separation between the slits fixed, but varies the width of the slits. The intensities of the peaks marked by and are and respectively. If the slits are made narrower while keeping the separation fixed, then the ratio
The intensity maximum at the central maximum on the diffraction pattern is due to_____ interference.
The intensity of secondary maxima less than the central bright band in diffraction pattern.
Why is the intensity of secondary maxima less than the central bright band in diffraction pattern?
For a diffraction from a single slit, the intensity of the central point is
Fraunhofer lines observed in the solar spectrum are due to
Fraunhoffer diffraction from a single slit is observed in the focal plane of a lens of focal length The slit width is The second minimum is observed at a distance of from the central maximum. Then the wavelength of light used is :-
Consider a Fraunhofer diffraction pattern due to circular aperture. In this case the diffraction pattern obtained at from lens. If the wavelength of light is and diameter of aperture is what is the separation between central disc and first secondary minimum?
The angular width of the central maximum of a diffraction pattern of a single slit pattern is the slit width being . A double slit experiment is now performed with the same wavelength of light and the same slit widths and it is found that the interference maximum is not formed, but all lower maxima are visible. The separation between the double slits is
The condition for observing Fraunhofer diffraction from a single slit is that the light wavefront incident on the slit should be :-
Consider fraunhofer diffraction pattern obtained with a single slit illuminated at normal incidence. At the angular position of the first diffraction minimum, the phase difference (in radians) between the wavelengths from the opposite edges of the slit is
A parallel beam of monochromatic light is incident normally on a slit. The diffraction pattern is observed on a screen placed at the focal plane of a convex lens. If the slit width is increased, the central maximum of the diffraction pattern will
The red light of wavelength from a distant source falls on a slit wide. Calculate the distance between the first two dark bands on each side of the central bright band in the diffraction pattern observed on a screen place from the slit.
A plane wavefront of wavelength is incident on a single slit of width a. The angular width of principal maximum is
Angular width of central maximum in the Fraunhoffer diffraction pattern of a slit is measured. The slit is illuminated by light of wavelength . When the slit is illuminated by light of another wavelength, then the angular width decreases by 30%. The same decrease in angular width of central maximum is obtained when the original apparatus is immersed in a liquid. The refractive index of the liquid will be
The angular size of the central maxima due to a single slit diffraction is (a slit width)
A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wave length is incident normally on a single narrow slit of width 0.001 mm. Light is focused by a convex lens on the screen placed on the focal plane. First minimum will be formed for the angle of diffraction
A screen is at a distance of 1m away from the aperture. If light of wavelength 500 nm falls on an aperture, then calculate area of first HPZ and radius of third HPZ
